🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In this article, we will discuss important Java Persistence API interview questions and answers.
JPA is just a specification that facilitates object-relational mapping to manage relational data in Java applications. It provides a platform to work directly with objects instead of using SQL statements.
JPA defines only specifications, it does not provide an implementation. JPA implementation is provided as a reference implementation by the vendors developing O/R Mappers such as Hibernate, EclipseLink, and Apache OpenJPA.
1. What is the Java Persistence API?
JPA stands for Jakarta Persistence API (JPA), formerly known as Java Persistence API.
JPA defines only specifications, it does not provide an implementation. JPA implementation is provided as a reference implementation by the vendors developing O/R Mappers such as Hibernate, EclipseLink, and Apache OpenJPA.
Read more about JPA at JPA Tutorial - Java Persistence API
Read more about Hibernate ORM Framework at Hibernate ORM Framework Tutorial
JPQL can retrieve information or data using the SELECT clause and can do bulk updates using the UPDATE clause and DELETE clause. EntityManager.createQuery() API will support querying language.
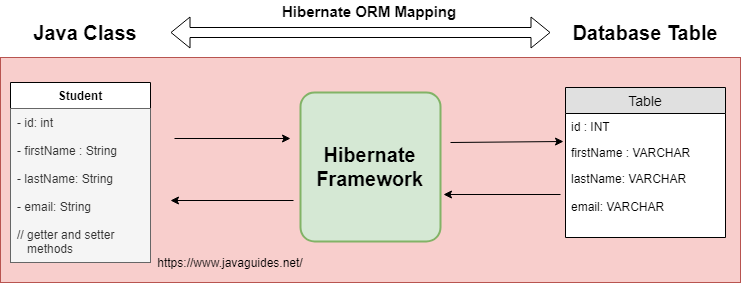
2. What is Object-Relational Mapping?
The term Object/Relational Mapping refers to the technique of mapping data from an object model representation to a relational data model representation (and vice versa).
For example, let's look at the below diagram showing the mapping between the Student java model and the database relational student table.
3. What are the advantages of JPA?
The advantages of JPA are given below.- The burden of interacting with the database reduces significantly by using JPA.
- The user programming becomes easy by concealing the O/R mapping and database access processing.
- The cost of creating the definition file is reduced by using annotations.
- We can merge the applications used with other JPA providers
- Using different implementations can add the features to the standard Implementation which can later be the part of JPA specification.
4. What is the Difference Between JPA and Hibernate?
As we know that JPA is just a specification, meaning there is no implementation. You can annotate your classes as much as you would like with JPA annotations, however, without an implementation, nothing will happen. Think of JPA as the guidelines that must be followed or an interface, while Hibernate's JPA implementation is code that meets the API as defined by the JPA specification and provides the under-the-hood functionality.
In short, JPA is the interface while Hibernate is the implementation.
Traditionally there have been multiple Java ORM solutions:
Each of the above implementations defines its own mapping definition or client API. The JPA expert group gathered the best of all these tools and so they created the Java Persistence API standard.
In short, JPA is the interface while Hibernate is the implementation.
Traditionally there have been multiple Java ORM solutions:
Each of the above implementations defines its own mapping definition or client API. The JPA expert group gathered the best of all these tools and so they created the Java Persistence API standard.
The benefit of this is that you can swap out Hibernate's implementation of JPA for another implementation of the JPA specification.
Read more at What is the Difference Between JPA and Hibernate?
5. Defining a JPA Entity Class
A JPA entity class is a POJO (Plain Old Java Object) class, i.e. an ordinary Java class that is marked (annotated) as having the ability to represent objects in the database. Conceptually this is similar to serializable classes, which are marked as having the ability to be serialized.
Read more about the JPA entity at JPA Entity Class Basics.
The Point Entity Class Example
The following Point class, which represents points in the plane, is marked as an entity class, and accordingly, provides the ability to store Point objects in the database and retrieve Point objects from the database:
@Entity
public class Point {
// Persistent Fields:
private int x;
private int y;
// Constructor:
Point (int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// Accessor Methods:
public int getX() { return this.x; }
public int getY() { return this.y; }
// String Representation:
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("(%d, %d)", this.x, this.y);
}
}
As you can see above, an entity class is an ordinary Java class. The only unique JPA addition is the @Entityannotation, which marks the class as an entity class.
6. What are the Requirements or Rules to Create JPA Entity Classes?
Let's discuss what are the rules or requirements to create a JPA entity class. An entity class must follow these requirements.
- The class must be annotated with the javax.persistence.Entity annotation.
- The class must have a public or protected, no-argument constructor. The class may have other constructors.
- The class must not be declared final. No methods or persistent instance variables must be declared final.
- If an entity instance is passed by value as a detached object, such as through a session bean's remote business interface, the class must implement the Serializable interface.
- Entities may extend both entity and non-entity classes, and non-entity classes may extend entity classes.
- Persistent instance variables must be declared private, protected, or package-private and can be accessed directly only by the entity class's methods. Clients must access the entity's state through accessor or business methods.
7. Java Persistence Query language
JPQL is Java Persistence Query Language defined in the JPA specification. It is used to create queries against entities to store in a relational database. JPQL is developed based on SQL syntax. But it won’t affect the database directly.JPQL can retrieve information or data using the SELECT clause and can do bulk updates using the UPDATE clause and DELETE clause. EntityManager.createQuery() API will support querying language.
8. Explain JPA Architecture or Explain the core classes and interfaces of JPA API?
Class Level Architecture
The following image shows the class-level architecture of JPA. It shows the core classes and interfaces of JPA.
Let's describe each of the units shown in the above architecture.
- EntityManagerFactory - This is a factory class of EntityManager. It creates and manages multiple EntityManager instances.
- EntityManager - It is an Interface, it manages the persistence operations on objects. It works like a factory for Query instance.
- Entity - Entities are the persistence objects, stored as records in the database.
- EntityTransaction - It has one-to-one relationship with EntityManager. For each EntityManager, operations are maintained by EntityTransaction class.
- Persistence - This class contains static methods to obtain EntityManagerFactory instance.
- Query - This interface is implemented by each JPA vendor to obtain relational objects that meet the criteria.
Read more about JPA architecture in-depth at JPA Architecture
9. What is an Entitymanager?
An EntityManager instance is associated with a persistence context. A persistence context is a set of entity instances in which for any persistent entity identity there is a unique entity instance. Within the persistence context, the entity instances and their lifecycle are managed.
The EntityManager API is used to create and remove persistent entity instances, to find entities by their primary key, and to query over entities.
In short, a connection to a database is represented by an EntityManager instance, which also provides functionality for performing operations on a database. Many applications require multiple database connections during their lifetime. For instance, in a web application, it is common to establish a separate database connection, using a separate EntityManager instance, for every HTTP request.
Read more about EntityManager in-depth at JPA EntityManager Interface with Example
10. Name required Steps to Persist JPA entity in a database?
Step1: First create an instance of EntityManagerFactory class using the Persistence class.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("PERSISTENCE");
- Persistence - Persistence is a bootstrap class that is used to obtain an EntityManagerFactory interface.
- createEntityManagerFactory() method - The role of this method is to create and return an EntityManagerFactory for the named persistence unit. Thus, this method contains the name of the persistence unit passed in the Persistence.xml file.
Step 2: Obtaining an EntityManager
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
- EntityManager - An EntityManager is an interface
- createEntityManager() method - It creates new application-managed EntityManager
Step 3: Using an EntityTransaction
Operations that modify database content, such as a store, update, and delete should only be performed within an active transaction.
Given an EntityManager, entityManager, it is very easy to begin a transaction:
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
- getTransaction() method - This method returns the resource-level EntityTransaction object.
- begin() method - This method is used to start the transaction.
The EntityManagerFactory is also used to close the database once we are finished using it:
entityManagerFactory.close();
When the connection to the database is no longer needed the EntityManager can be closed:
entityManager.close();
11. What are the steps to insert an entity?
12. What are the steps to find an entity?
13. What are the steps to update an entity?
14. What are the steps to delete an entity?
15. What Data Types Are Allowed in the Attributes of the Entity Class (Fields or Properties)?
The persistent state of an entity can be accessed through either the entity's instance variables or properties. The fields or properties must be of the following Java language types:
- java.lang.String
- Other serializable types, including:
- Wrappers of Java primitive types
- java.math.BigInteger
- java.math.BigDecimal
- java.util.Date
- java.util.Calendar
- java.sql.Date
- java.sql.Time
- java.sql.TimeStamp
- User-defined serializable types
- byte[]
- Byte[]
- char[]
- Character[]
- Other entities and/or collections of entities
16. What Is the Embeddable Class in JPA?
An embeddable class is a class that is not used by itself, only as part of one or more Entity classes. An entity class can contain both single embedded classes and collections of such classes. Also, such classes can be used as keys or map values. At runtime, each embedded class belongs to only one object of the Entity class and cannot be used to transfer data between the objects of the Entity classes (that is, such a class is not a common data structure for different objects).
In general, such a class serves to make the definition of common attributes for several entities, we can assume that JPA simply embeds into the Entity instead of an object of this class, the attributes it contains.
Check out a complete example at JPA- Using @Embeddable and @Embedded Annotation
17. What are the different types of entity mapping?
Following are the types of object-relational mapping: -- One-to-one mapping: The one-to-one mapping represents a single-valued association where an instance of one entity is associated with an instance of another entity. In this type of association, one instance of the source entity can be mapped with at most one instance of the target entity.
- One-To-Many mapping: The One-To-Many mapping comes into the category of collection-valued association where an entity is associated with a collection of other entities. In this type of association, the instance of one entity can be mapped with any number of instances of another entity.
- Many-to-one mapping: The Many-To-One mapping represents a single-valued association where a collection of entities can be associated with a similar entity. In the relational database, more than one row of an entity can refer to the same row of another entity.
- Many-to-many mapping: The Many-To-Many mapping represents a collection-valued association where any number of entities can be associated with a collection of other entities. In the relational database, more than one row of one entity can refer to more than one row of another entity.
18. What is the JPA Cascade Types?
JPA allows you to propagate the state transition from a parent entity to a child. For this purpose, the JPA javax.persistence.CascadeType defines various cascade types:
- ALL - cascades all entity state transitions
- PERSIST - cascades the entity persist operation.
- MERGE - cascades the entity merge operation.
- REMOVE - cascades the entity remove operation.
- REFRESH - cascades the entity refresh operation.
- DETACH - cascades the entity detach operation.
Entities that use relationships often have dependencies on the existence of the other entity in the relationship. For example, a line item is part of an order; if the order is deleted, the line item also should be deleted. This is called a cascade delete relationship.
Read more about JPA cascade types with a complete example at Guide to JPA and Hibernate Cascade Types
19. What are the features of JPQL?
Some of the essential features of JPQL are: -- It is simple and robust.
- It is a platform-independent query language.
- JPQL queries can be declared statically into metadata or can also be dynamically built-in code.
- It can be used with any database such as MySQL, or Oracle.
20. What is the JPA Primary Key Generation Strategies?
The JPA specification supports 4 different primary key generation strategies which generate the primary key values programmatically or use database features, like auto-incremented columns or sequences.
1. GenerationType.AUTO
2. GenerationType.IDENTITY
3. GenerationType.SEQUENCE
4.GenerationType.TABLE
Know more about these primary key generation strategies with examples at Hibernate/JPA - Primary Key Generation Strategies
21. Explain JPA Inheritance Strategies?
JPA specification provides several strategies:
- MappedSuperclass - Inheritance is implemented in the domain model only without reflecting it in the database schema. See MappedSuperclass.
- Single table - The domain model class hierarchy is materialized into a single table that contains entities belonging to different class types. See Single table.
- Joined table - The base class and all the subclasses have their own database tables and fetching a subclass entity requires a join with the parent table as well. See Joined table.
- Table per class - Each subclass has its own table containing both the subclass and the base class properties.
Read more at Hibernate/JPA - Inheritance Mapping.
Learn everything about JPA at JPA Tutorial - Java Persistence API
Leave a comment if you have other interview questions regarding Java Persistence API so that I will add this list which will help others to prepare for their interview.
<< Back to JPA Tutorial
Related Java Interview Articles
- Spring Boot Interview Questions
- Java Tricky Coding Interview Questions
- Java String Interview Questions
- Java String Tricky Coding Questions
- Java main() Method Interview Questions
- Java 8 Interview Questions
- Top 10 Spring MVC Interview Questions
- Java Array Interview Questions and Answers
- Java OOPS Tricky Coding Questions
- Java Programs Asked in Interview
- OOPS Interview Questions and Answers
- Hibernate Interview Questions
- JPA Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Design Patterns Interview Questions
- Spring Core Interview Questions
- Java Exception Handling Interview
My Top and Bestseller Udemy Courses. The sale is going on with a 70 - 80% discount. The discount coupon has been added to each course below:

Build REST APIs with Spring Boot 4, Spring Security 7, and JWT
🆕 High-Demand
80–90% OFF
![[NEW] Learn Apache Maven with IntelliJ IDEA and Java 25 [NEW] Learn Apache Maven with IntelliJ IDEA and Java 25](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/6852721_b512_2.jpg)
[NEW] Learn Apache Maven with IntelliJ IDEA and Java 25
🆕 High-Demand
80–90% OFF

ChatGPT + Generative AI + Prompt Engineering for Beginners
🚀 Trending Now
80–90% OFF

Spring 7 and Spring Boot 4 for Beginners (Includes 8 Projects)
🔥 Bestseller
80–90% OFF
Available in Udemy for Business
Available in Udemy for Business

Building Real-Time REST APIs with Spring Boot - Blog App
🔥 Bestseller
80–90% OFF
Available in Udemy for Business
Available in Udemy for Business

Building Microservices with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
🌟 Top Rated
80–90% OFF
Available in Udemy for Business
Available in Udemy for Business
![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)
Java Full-Stack Developer Course with Spring Boot and React JS
🔥 Bestseller
80–90% OFF
Available in Udemy for Business
Available in Udemy for Business

Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding
🌟 Top Rated
80–90% OFF

Testing Spring Boot Application with JUnit and Mockito
🔥 Bestseller
80–90% OFF
Available in Udemy for Business
Available in Udemy for Business

Spring Boot Thymeleaf Real-Time Web Application - Blog App
🔥 Bestseller
80–90% OFF
Available in Udemy for Business
Available in Udemy for Business

Master Spring Data JPA with Hibernate
🔥 Bestseller
80–90% OFF
Available in Udemy for Business
Available in Udemy for Business

Spring Boot + Apache Kafka Course - The Practical Guide
🎓 Student Favorite
80–90% OFF
Available in Udemy for Business
Available in Udemy for Business







Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment