🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In this post, I am going to explain the differences between Core Java and Advanced Java, and at the end of this post, you will be able to understand what exactly Core Java and Advanced Java are.
Core Java
Core Java refers to the fundamental and essential parts of the Java programming language that form the building blocks of Java development.Concepts: Includes the basic principles of object-oriented programming (OOP), such as classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, etc.
Syntax: Understanding the basic syntax, data types, control structures, loops, etc.
Libraries: Utilizes core libraries, mainly those within java.lang, java.util, and similar basic packages.
JVM Understanding: Understanding how Java code is compiled into bytecode, and how it runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Usage: Suitable for building fundamental applications and forms the base for all Java development.
Core Java Important Topics for your reference:
- Java Syntax
- Data Types
- Variables
- Operators
- Expressions
- Control Flow Statements (if, switch, loops)
- Arrays
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) - Classes, Objects, Inheritance, Polymorphism, Encapsulation and Abstraction
- Abstract Classes and Interfaces
- Exception Handling (try, catch, finally) and Errors
- File Input/Output
- Java Streams
- Collections Framework - List, Set, Map, and its implementations
- Generics
- Multithreading, Synchronization
- String Handling
- Wrapper Classes
- Enums
- Java Date and Time
- Annotations
- Lambda Expressions
Advanced Java
Advanced Java builds on the principles of Core Java and introduces more complex and specialized concepts.Web Development: Includes technologies for web development, like Servlets, JavaServer Pages (JSP), and frameworks like Spring.
Enterprise Development: Understanding Java Enterprise Edition (JEE) with components like Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB). In Java development, most companies use Spring Framework to build enterprise applications. Spring Framework is a replacement for EJB.
Networking: Understanding sockets, RMI, and other network-related programming.
Concurrency: In-depth understanding of multi-threading, synchronization, and concurrent collections.
Design Patterns: Introduction to more complex design patterns and architecture.
Usage: Suitable for building robust, scalable, and complex applications, including web applications, distributed systems, etc.
Advanced Java Important Topics for your reference:
- JDBC
- Servlets
- JavaServer Pages (JSP)
- JavaServer Faces (JSF)
- Spring (Core, MVC, Boot)
- Hibernate
- Networking
- Remote Method Invocation (RMI)
- Enterprise Java (Java EE)
- Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB)
- Java Persistence API (JPA)
- Java Transaction API (JTA)
- Java Message Service (JMS)
- Design Patterns
- JUnit
- Mockito
- Web Services (SOAP, REST)
- JavaFX for GUI
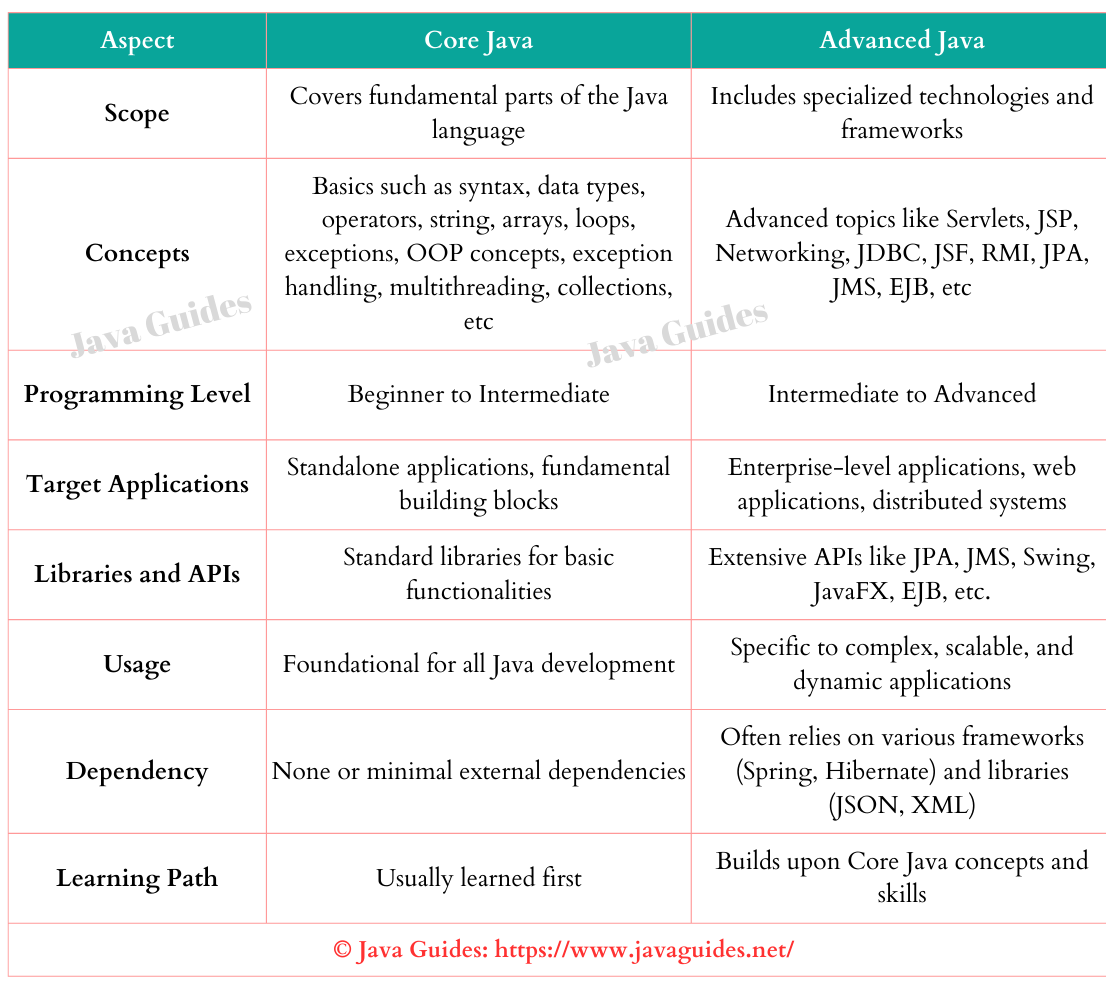
| Aspect | Core Java | Advanced Java |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Covers fundamental parts of the Java language | Includes specialized technologies and frameworks |
| Concepts | Basics such as syntax, data types, operators, string, arrays, loops, exceptions, OOP concepts, exception handling, multithreading, collections, etc | Advanced topics like Servlets, JSP, Networking, JDBC, JSF, RMI, JPA, JMS, EJB, etc |
| Programming Level | Beginner to Intermediate | Intermediate to Advanced |
| Target Applications | Standalone applications, fundamental building blocks | Enterprise-level applications, web applications, distributed systems |
| Libraries and APIs | Standard libraries for basic functionalities | Extensive APIs like JPA, JMS, Swing, JavaFX, EJB, etc. |
| Usage | Foundational for all Java development | Specific to complex, scalable, and dynamic applications |
| Dependency | None or minimal external dependencies | Often relies on various frameworks (Spring, Hibernate) and libraries (JSON, XML) |
| Learning Path | Usually learned first | Builds upon Core Java concepts and skills |
Conclusion
Core Java refers to the essential parts of the Java programming language that form the foundation for all Java development. Core Java is typically what's taught to beginners and is used in standalone applications or as the building blocks for more complex systems.
Advanced Java encompasses a broader set of specialized technologies, libraries, and frameworks that enable the development of more complex, scalable, and dynamic applications.




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)










Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment