🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
The SortedSet interface in Java is a member of the Java Collections Framework and extends the Set interface.
Important Key Points about the SortedSet Interface
Here are some key points about the SortedSet interface:
Sorting:
SortedSet is a Set that maintains its elements in ascending order. The sorting can be based on either natural order or it can be customized through a comparator at SortedSet creation time.
Ordering:
Elements inserted into the SortedSet need to implement the Comparable interface. The elements are ordered by using their compareTo() method unless a Comparator is provided at set creation time.
No Duplicates:
Just like any other set, SortedSet doesn't allow duplicates.
Methods:
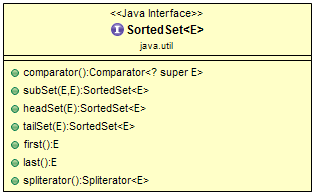
In addition to standard Set operations, the SortedSet interface provides operations for the following: Range view — allows arbitrary range operations on the sorted set.
Endpoints — returns the first or last element in the sorted set.
Subinterfaces and Implementations:
The primary SortedSet implementation in the Java Collections Framework is TreeSet.
Null Elements:
SortedSet implementations (like TreeSet) don't permit the use of null elements, because null is not comparable.
Use-cases:
SortedSet is ideal when you want to store unique elements in a sorted manner.
Thread Safety:
SortedSet implementations are not thread-safe, but you can make them thread-safe using synchronized wrappers obtained from the Collections utility class.
Iterators:
The iterator provided in the SortedSet interface iterates over the elements in the set in ascending order.
Head, Tail, and Subsets:
The SortedSet interface provides methods to get subsets from the set, which are still sorted according to the set's ordering.
Remember, SortedSet is an interface and you cannot instantiate interfaces. Therefore, you need to either use its subclass or a class that implements the SortedSet interface to create an object.
SortedSet Interface Example
This example demonstrates some important methods of the SortedSet Interface using TreeSet implementation class.import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.SortedSet;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class CreateTreeSetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a TreeSet
SortedSet<String> fruits = new TreeSet<>();
// Adding new elements to a TreeSet
fruits.add("Banana");
fruits.add("Apple");
fruits.add("Pineapple");
fruits.add("Orange");
// Returns the first (lowest) element currently in this set.
String first = fruits.first();
System.out.println("First element : " + first);
// Returns the last (highest) element currently in this set.
String last = fruits.last();
System.out.println("Last element : " + last);
// Returns the comparator used to order the elements in this set, or
// null if this set uses the natural ordering of its elements.
Comparator<?> comparator = fruits.comparator();
SortedSet<String> tailSet = fruits.tailSet("Orange");
System.out.println("tailSet :" + tailSet);
}
}
Output:
First element : Apple
Last element : Pineapple
tailSet :[Orange, Pineapple]SortedSet Interface Hierarchy Diagram
SortedSet Interface APIs/Methods
SortedSet Interface Implementation Class
TreeSet ClassRelated Collections Framework Interfaces
- Collections Framework - The Collection Interface
- Collections Framework - The Set Interface
- Collections Framework - The SortedSet Interface
- Collections Framework - The List Interface
- Collections Framework - The Queue Interface
- Collections Framework - The Deque Interface
- Collections Framework - The Map Interface
- Collections Framework - The SortedMap Interface




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)











Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment