🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
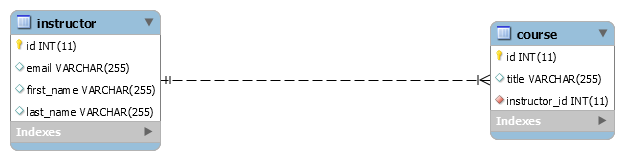
In this tutorial, we will learn how to implement step-by-step one-to-many bidirectional entity mapping using JPA and Hibernate, and the MySQL database.
The @OneToMany and @ManyToOne JPA annotations are used to link one-to-many bidirectional entity mapping.
There are two types of one-to-many associations -
- Unidirectional → In this type of association, only the source entity has a relationship field that refers to the target entity. We can navigate this type of association from one side.
- Bidirectional → In this type of association, each entity (i.e. source and target) has a relationship field that refers to each other. We can navigate this type of association from both sides.
In this example, we implement step-by-step one-to-many bidirectional entity mapping using JPA and Hibernate, and the MySQL database.
Overview
We will implement CRUD (create/save, read, update, delete) operations for Instructor and Course entities. You can download the source code of this example at my GitHub repository (link given at end of this article).
For Instructor DAO CRUD operations:
void saveInstructor(Instructor instructor);
void updateInstructor(Instructor instructor);
void deleteInstructor(int id);
Instructor getInstructor(int id);
For Course DAO CRUD operations:
void saveCourse(Course course);
void updateCourse(Course course);
void deleteCourse(int id);
Course getCourse(int id);
Development Steps
- Create a Simple Maven Project
- Project Directory Structure
- Add jar Dependencies to pom.xml
- Creating the JPA Entities(Persistent classes)
- Create Hibernate DAO Classes
- Create a Hibernate configuration file - HibernateUtil.java (Java Configuration)
- Create the Main class and Run an Application
1. Create a Simple Maven Project
Use the How to Create a Simple Maven Project in Eclipse article to create a simple Maven project in Eclipse IDE.
2. Project Directory Structure
Let's create a packaging structure for the above-created simple maven project:
2. POM Dependencies
Let's add Hibernate and MySQL dependencies to pom.xml:
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-tutorial</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>hibernate-one-to-many-bi-example</artifactId>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.32</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>6.1.7.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/java</sourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>17</source>
<target>17</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
3. Creating the JPA Entities(Persistent classes)
Let's create JPA entities that we map with database tables.The @OneToMany and @ManyToOne JPA annotations are used to link one-to-many bidirectional entity mapping.
Instructor JPA Entity
package net.javaguides.hibernate.entity;
import java.util.List;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "instructor")
public class Instructor {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "instructor", cascade = { CascadeType.PERSIST, CascadeType.MERGE, CascadeType.DETACH,
CascadeType.REFRESH })
private List<Course> courses;
public Instructor() {
}
public Instructor(String firstName, String lastName, String email) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public List<Course> getCourses() {
return courses;
}
public void setCourses(List<Course> courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
}
Course JPA Entity
package net.javaguides.hibernate.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "course")
public class Course {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "title")
private String title;
@ManyToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "instructor_id")
private Instructor instructor;
public Course() {
}
public Course(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public Instructor getInstructor() {
return instructor;
}
public void setInstructor(Instructor instructor) {
this.instructor = instructor;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Course [id=" + id + ", title=" + title + "]";
}
}
- @Table maps the entity with the table. If no @Table is defined, the default value is used: the class name of the entity.
- @Id declares the identifier property of the entity.
- @Column maps the entity's field with the table's column. If @Column is omitted, the default value is used: the field name of the entity.
- @OneToMany and @ManyToOne define a one-to-many and many-to-one relationship between 2 entities.
- @JoinColumn indicates the entity is the owner of the relationship: the corresponding table has a column with a foreign key to the referenced table. mappedBy indicates the entity is the inverse of the relationship.
4. Create Hibernate DAO Classes
InstructorDao.java
The InstructorDao class provides the implementation of DAO CRUD methods for the Instructor entity:
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.entity.Instructor;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.util.HibernateUtil;
public class InstructorDao {
public void saveInstructor(Instructor instructor) {
Transaction transaction = null;
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
// start a transaction
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// save the student object
session.save(instructor);
// commit transaction
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void updateInstructor(Instructor instructor) {
Transaction transaction = null;
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
// start a transaction
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// save the student object
session.update(instructor);
// commit transaction
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void deleteInstructor(int id) {
Transaction transaction = null;
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
// start a transaction
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// Delete a instructor object
Instructor instructor = session.get(Instructor.class, id);
if (instructor != null) {
session.delete(instructor);
System.out.println("instructor is deleted");
}
// commit transaction
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Instructor getInstructor(int id) {
Transaction transaction = null;
Instructor instructor = null;
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
// start a transaction
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// get an instructor object
instructor = session.get(Instructor.class, id);
// commit transaction
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
return instructor;
}
}CourseDao.java
The CourseDao class provides the following implementation DAO CRUD methods for the Course entity:
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.entity.Course;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.util.HibernateUtil;
public class CourseDao {
public void saveCourse(Course course) {
Transaction transaction = null;
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
// start a transaction
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// save the student object
session.save(course);
// commit transaction
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void updateCourse(Course course) {
Transaction transaction = null;
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
// start a transaction
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// save the student object
session.update(course);
// commit transaction
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void deleteCourse(int id) {
Transaction transaction = null;
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
// start a transaction
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// Delete a course object
Course course = session.get(Course.class, id);
if (course != null) {
session.delete(course);
System.out.println("course is deleted");
}
// commit transaction
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Course getCourse(int id) {
Transaction transaction = null;
Course course = null;
try (Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
// start a transaction
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
// get an course object
course = session.get(Course.class, id);
// commit transaction
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
return course;
}
}5. Create a Hibernate configuration file - HibernateUtil.java (Java Configuration)
The HibernateUtil Java configuration file contains information about the database and mapping file.
Let's create a HibernateUtil file and write the following code in it.
package net.javaguides.hibernate.util;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Environment;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.entity.Course;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.entity.Instructor;
/**
* Java based configuration
* @author ramesh Fadatare
*
*/
public class HibernateUtil {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if (sessionFactory == null) {
try {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// Hibernate settings equivalent to hibernate.cfg.xml's properties
Properties settings = new Properties();
settings.put(Environment.DRIVER, "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
settings.put(Environment.URL, "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate_db?useSSL=false");
settings.put(Environment.USER, "root");
settings.put(Environment.PASS, "root");
settings.put(Environment.DIALECT, "org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect");
settings.put(Environment.SHOW_SQL, "true");
settings.put(Environment.CURRENT_SESSION_CONTEXT_CLASS, "thread");
settings.put(Environment.HBM2DDL_AUTO, "create-drop");
configuration.setProperties(settings);
configuration.addAnnotatedClass(Instructor.class);
configuration.addAnnotatedClass(Course.class);
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder()
.applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
System.out.println("Hibernate Java Config serviceRegistry created");
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
return sessionFactory;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sessionFactory;
}
}
6. Create the Main class and Run an Application
Let's test a Hibernate application to connect to the MySQL database.
package net.javaguides.hibernate;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.dao.CourseDao;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.dao.InstructorDao;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.entity.Course;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.entity.Instructor;
public class ManApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InstructorDao instructorDao = new InstructorDao();
CourseDao courseDao = new CourseDao();
Instructor instructor = new Instructor("Ramesh", "Fadatare", "ramesh@javaguides.com");
instructorDao.saveInstructor(instructor);
// create some courses
Course tempCourse1 = new Course("Air Guitar - The Ultimate Guide");
tempCourse1.setInstructor(instructor);
courseDao.saveCourse(tempCourse1);
Course tempCourse2 = new Course("The Pinball Masterclass");
tempCourse2.setInstructor(instructor);
courseDao.saveCourse(tempCourse2);
}
}
7. Output
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we successfully built a project from scratch and learned how to map a one-to-many bidirectional database relationship using Hibernate/JPA.
Get the source code of this tutorial on my GitHub Repository.
You might also be interested in checking out the following articles on JPA and Hibernate -




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)












Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment