🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In this article, we will discuss how to use Jakarta Persistence API (JPA) to perform CRUD operations against the MySQL database. For this example, we will use the Hibernate framework as JPA implementation.
Learn complete JPA at JPA Tutorial - Jakarta Persistence API
Learn Hibernate ORM Framework at Hibernate Tutorial
What are CRUD operations in JPA?
The CRUD stands for Create, Retrieve (Read), Update, and Delete operations on an Entity.
The JPA has an EntityManager interface that is associated with a persistence context. It is used to interact with the persistence context.
Here are a few important methods of EntityManager that are used to perform the CRUD operations.
- persist(): This method is used to persist a managed Entity.
- remove(): This method is used to remove an Entity from the persistence context.
- merge(): This method is used to save the current state of the Entity to the persistence context.
- find(): This method is used to load an Entity based on its primary key.
I have written a separate article on an EntityManager interface, just check out at JPA EntityManager interface with an example.
The Jakarta Persistence API is a Java specification for managing, persisting, and accessing data between objects and relational databases.
Hibernate is an ORM (Object Relational Mapping) tool that implements JPA specifications. In this example, we will use Hibernate as a JPA provider.
In this post, we will show you how to create or configure a simple JPA application with Hibernate.
Technologies and tools used
- Hibernate 6.1.7.Final
- JPA 3.0
- IDE - Eclipse
- Maven 3.5.3
- Java 17
- MySQL - 8.0.32
Let's start developing step by step Hibernate application using Maven as a project management and build tool.
Development Steps
- Create a Simple Maven Project
- Project Directory Structure
- Add jar Dependencies to pom.xml
- Creating the JPA Entity Class(Persistent class)
- JPA CRUD Operations
- Create a JPA configuration file
- Create a JPA helper class
- Create the Main class and Run an Application
1. Create a Simple Maven Project
Use the How to Create a Simple Maven Project in Eclipse article to create a simple Maven project in Eclipse IDE.3. Add jar Dependencies to pom.xml
<<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-tutorial</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>jpa-crud-example</artifactId>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.32</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate/hibernate-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>6.1.7.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/java</sourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>17</source>
<target>17</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
4. Creating the JPA Entity Class(Persistent class)
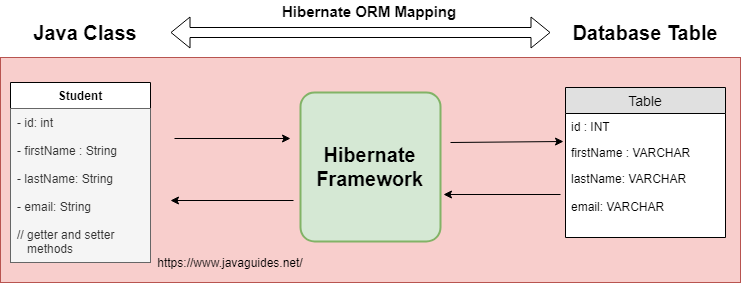
The below diagram shows the Student JPA entity that is mapped to a database students table.
Well, let's create a Student entity class under net.javaguides.hibernate.entity package as follows.
package net.javaguides.hibernate.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String firstName, String lastName, String email) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + "]";
}
}
If you are new to the JPA entity then read my article here to know about JPA entity basics.
5. JPA CRUD Operations
Let's use EntityManager interface methods to create CRUD Operations against a database.
package net.javaguides.hibernate;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityTransaction;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.entity.Student;
import net.javaguides.hibernate.util.JPAUtil;
/**
* JPA CRUD Operations
* @author Ramesh Fadatare
*
*/
public class CRUDOperations {
public void insertEntity() {
EntityManager entityManager = JPAUtil.getEntityManagerFactory().createEntityManager();
EntityTransaction entityTransaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
entityTransaction.begin();
Student student = new Student("Ramesh", "Fadatare", "rameshfadatare@javaguides.com");
entityManager.persist(student);
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
entityManager.close();
}
public void findEntity() {
EntityManager entityManager = JPAUtil.getEntityManagerFactory().createEntityManager();
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
Student student = entityManager.find(Student.class, 1);
System.out.println("student id :: " + student.getId());
System.out.println("student firstname :: " + student.getFirstName());
System.out.println("student lastname :: " + student.getLastName());
System.out.println("student email :: " + student.getEmail());
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
entityManager.close();
}
public void updateEntity() {
EntityManager entityManager = JPAUtil.getEntityManagerFactory().createEntityManager();
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
Student student = entityManager.find(Student.class, 1);
System.out.println("student id :: " + student.getId());
System.out.println("student firstname :: " + student.getFirstName());
System.out.println("student lastname :: " + student.getLastName());
System.out.println("student email :: " + student.getEmail());
// The entity object is physically updated in the database when the transaction
// is committed
student.setFirstName("Ram");
student.setLastName("jadhav");
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
entityManager.close();
}
public void removeEntity() {
EntityManager entityManager = JPAUtil.getEntityManagerFactory().createEntityManager();
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
Student student = entityManager.find(Student.class, 1);
System.out.println("student id :: " + student.getId());
System.out.println("student firstname :: " + student.getFirstName());
System.out.println("student lastname :: " + student.getLastName());
System.out.println("student email :: " + student.getEmail());
entityManager.remove(student);
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
entityManager.close();
}
}
6. Create a JPA configuration file
Create an XML file named persistence.xml under the src/main/java/META-INF folder and write the following code in it.
<persistence
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_1.xsd"
version="2.1">
<persistence-unit name="PERSISTENCE">
<description> Hibernate JPA Configuration Example</description>
<provider>org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider</provider>
<class>net.javaguides.hibernate.entity.Student</class>
<properties>
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.driver"
value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate_db" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.user" value="root" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.password"
value="root" />
<property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true" />
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create-drop" />
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
7. Create a JPA helper class
Create a helper class to bootstrap a JPA EntityManagerFactory.
package net.javaguides.hibernate.util;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import jakarta.persistence.Persistence;
public class JPAUtil {
private static final String PERSISTENCE_UNIT_NAME = "PERSISTENCE";
private static EntityManagerFactory factory;
public static EntityManagerFactory getEntityManagerFactory() {
if (factory == null) {
factory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory(PERSISTENCE_UNIT_NAME);
}
return factory;
}
public static void shutdown() {
if (factory != null) {
factory.close();
}
}
}
8. Create a main class and run an application
Here is the main class to persist the student object using the EntityManager#persist method.
MainApp.java
package net.javaguides.hibernate;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CRUDOperations crudOperations = new CRUDOperations();
crudOperations.insertEntity();
crudOperations.findEntity();
crudOperations.updateEntity();
crudOperations.removeEntity();
}
}
Output
Learn complete JPA at Jakarta Tutorial - Java Persistence API
Learn Hibernate ORM Framework at Hibernate Tutorial




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)












if c, u, d have error, not commit. Why not have rollback()? Thank you !!!
ReplyDelete