🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
🚀 Introduction
Spring Boot provides multiple stereotype annotations (@Service, @Repository, @Controller, and @Component) to mark beans for dependency injection. But when should you use each of them?
This guide explains:
✔ Differences between @Service, @Repository, @Controller, and @Component
✔ Their specific use cases
✔ How Spring Boot manages them in the application context
1️⃣ @Component — The Generic Stereotype
The @Component annotation is the most generic annotation used for marking a class as a Spring-managed bean.
📌 When to Use @Component?
- When a class does not fit into
@Service,@Repository, or@Controllercategories. - For custom utility classes, helper services, or third-party integrations.
✅ Example: Defining a General Component
@Component
public class EmailUtility {
public void sendEmail(String recipient, String message) {
System.out.println("Sending email to: " + recipient);
}
}📌 Spring will register EmailUtility as a bean, allowing it to be injected into other components.
2️⃣ @Service — The Business Logic Layer
The @Service annotation is a specialized version of @Component, intended for service layer beans that contain business logic.
📌 When to Use @Service?
- For classes that handle business logic.
- When performing complex calculations, data transformation, or transaction management.
✅ Example: Defining a Service Layer
@Service
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
public ProductService(ProductRepository productRepository) {
this.productRepository = productRepository;
}
public List<Product> getAllProducts() {
return productRepository.findAll();
}
}📌 Spring treats @Service differently when enabling transaction management (@Transactional).
3️⃣ @Repository — The Data Access Layer
The @Repository annotation is a specialized version of @Component, intended for data access layer (DAO) classes.
📌 When to Use @Repository?
- For classes that directly interact with the database.
- When working with Spring Data JPA or JDBC.
- Enables automatic exception translation for database errors into Spring’s
DataAccessException.
✅ Example: Defining a Repository Layer
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long> {
}📌 Spring Data JPA automatically detects this interface as a repository, even without @Repository.
4️⃣ @Controller — The Presentation Layer
The @Controller annotation is a specialized version of @Component, intended for handling web requests in Spring MVC applications.
📌 When to Use @Controller?
- For handling HTTP requests in a Spring MVC web application.
- When returning views (Thymeleaf, JSP, etc.) instead of raw JSON.
✅ Example: Defining a Controller
@Controller
public class WebController {
@GetMapping("/home")
public String home(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Welcome to Spring Boot!");
return "home"; // Returns a view template (Thymeleaf/JSP)
}
}📌 @Controller is typically used when working with UI frameworks (Thymeleaf, JSP).
5️⃣ @RestController — The REST API Controller
The @RestController annotation is a combination of @Controller and @ResponseBody.
📌 When to Use @RestController?
- For RESTful APIs that return JSON or XML responses.
✅ Example: Defining a REST API Controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/products")
public class ProductController {
private final ProductService productService;
public ProductController(ProductService productService) {
this.productService = productService;
}
@GetMapping
public List<Product> getProducts() {
return productService.getAllProducts();
}
}📌 Unlike @Controller, @RestController automatically converts responses to JSON.
6️⃣ Key Differences Between @Component, @Service, @Repository, and @Controller
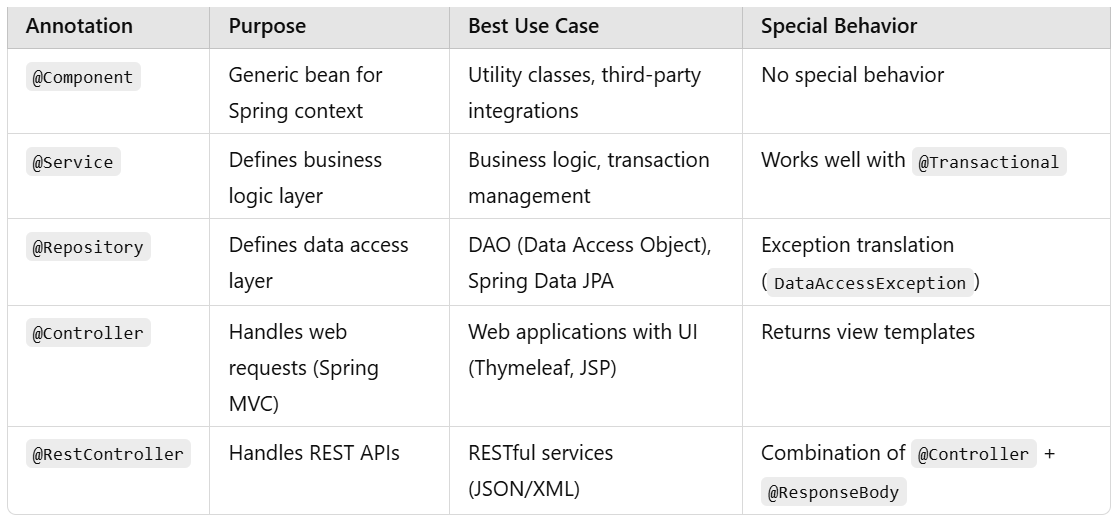
7️⃣ Summary — When to Use Which Annotation?
✔ Use @Component when none of the other annotations fit.
✔ Use @Service for business logic processing.
✔ Use @Repository for database operations and Spring Data JPA.
✔ Use @Controller for web applications returning views.
✔ Use @RestController for REST APIs that return JSON responses.
❓ FAQs — Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I replace @Service with @Component?
Yes! Since @Service is a specialization of @Component, Spring will still detect the bean. However, @Service improves readability and is recommended for service layer beans.
2. Is @Repository required for Spring Data JPA?
No. Spring Data JPA automatically detects JpaRepository implementations without needing @Repository. However, you can still use it for clarity.
3. What is the difference between @Controller and @RestController?
@Controlleris used for web applications and returns view templates.@RestControlleris used for REST APIs and returns JSON responses.
4. Can I use @RestController instead of @Controller?
Yes, but @RestController is only for REST APIs. If you are building a web application with a UI, use @Controller.
🚀 Understanding these annotations will help you structure your Spring Boot application effectively!
My Top and Bestseller Udemy Courses. The sale is going on with a 70 - 80% discount. The discount coupon has been added to each course below:

Build REST APIs with Spring Boot 4, Spring Security 7, and JWT
![[NEW] Learn Apache Maven with IntelliJ IDEA and Java 25 [NEW] Learn Apache Maven with IntelliJ IDEA and Java 25](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/6852721_b512_2.jpg)
[NEW] Learn Apache Maven with IntelliJ IDEA and Java 25

ChatGPT + Generative AI + Prompt Engineering for Beginners

Spring 7 and Spring Boot 4 for Beginners (Includes 8 Projects)
Available in Udemy for Business

Building Real-Time REST APIs with Spring Boot - Blog App
Available in Udemy for Business

Building Microservices with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Available in Udemy for Business
![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)
Java Full-Stack Developer Course with Spring Boot and React JS
Available in Udemy for Business

Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding

Testing Spring Boot Application with JUnit and Mockito
Available in Udemy for Business

Spring Boot Thymeleaf Real-Time Web Application - Blog App
Available in Udemy for Business

Master Spring Data JPA with Hibernate
Available in Udemy for Business

Spring Boot + Apache Kafka Course - The Practical Guide
Available in Udemy for Business






Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment