🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
Welcome to the first part of my full-stack app development series with Spring Boot, Hibernate, MySQL, and React JS.
This completes the development of Spring boot CRUD Rest APIs.
❮ Previous
Next ❯
In this part 1, we will create a Spring boot project in Eclipse STS IDE and develop a CRUD RESTFul APIs using Spring boot.
Recommended tutorial - Learn Spring boot at https://www.javaguides.net/p/spring-boot-tutorial.html
YouTube Playlist
I suggest you to watch this series on my YouTube channel to understand more about this full-stack app:
Creating the Backend Application using Spring Boot
Following are five REST APIs (Controller handler methods), we will develop for Employee resource.
1. Create Spring Boot Project in Eclipse STS IDE
Use the below guide to create a Spring boot project in Eclipse STS IDE:
3. Maven Dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
The spring-boot-starter-web Starter:
We use spring-boot-starter-web dependency to develop RESTful web services.
This dependency provides tomcat server as the default embedded container:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
The spring-boot-starter-data-jpa Starter:
We use spring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependency to talk with the database.
This dependency internally uses Hibernate as the default JPA provider:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>The MySQL connector dependency:
We use below MySQL connector dependency to connect the Spring boot application with the MySQL database:
<dependency> <groupId>com.mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>
4. Configuring MySQL Database
Let's configure application.properties to connect to your MySQL database.
Note that we have added MySQL dependency to pom.xml so spring boot will auto-configure all database-related beans and configurations internally.
Let's open an application.properties file and add the following database configuration to it:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/employee_management_system?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
You need to create a database in MySQL server with the following command:
create database employee_management_system
Change the above configuration such as JDBC URL, username, and password as per your environment.
Hibernate will automatically create database tables so you only need to manually create the database and configure an application.properties file.
5. Create JPA Entity - Employee.java
Let's create a new package called net.javaguides.springboot.model, within this package, create a class called Employee and add the following code to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email_id")
private String emailId;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String firstName, String lastName, String emailId) {
super();
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.emailId = emailId;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmailId() {
return emailId;
}
public void setEmailId(String emailId) {
this.emailId = emailId;
}
}
- All your domain models must be annotated with @Entity annotation. It is used to mark the class as a persistent Java class.
- @Table annotation is used to provide the details of the table that this entity will be mapped to.
- @Id annotation is used to define the primary key.
- @GeneratedValue annotation is used to define the primary key generation strategy.
- @Column annotation is used to define the properties of the column that will be mapped to the annotated field.
6. Create a Spring Data Repository - EmployeeRepository.java
Let’s create the repository now. First, create a new package called repository inside the base package net.javaguides.springboot. Then, create an interface called EmployeeRepository and extend it from JpaRepository -
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long>{
}
7. Creating Custom Business Exception
We’ll define the Rest APIs for creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting an Employee in the next section.
The APIs will throw a ResourceNotFoundException whenever an Employee with a given id is not found in the database.
Let's create a package named exception inside base package net.javaguides.springboot. Then create a new class called ResourceNotFoundException with the following content:
package net.javaguides.springboot.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1 L;
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
8. Create Spring Rest Controller - EmployeeController.java
We’ll now create the REST APIs for creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting an Employee.
First, create a new package controller inside com.javaguides.springboot. Then, create a new class EmployeeController with the following contents -
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import net.javaguides.springboot.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.EmployeeRepository;
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:3000")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
// get all employees
@GetMapping("/employees")
public List < Employee > getAllEmployees() {
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
// create employee rest api
@PostMapping("/employees")
public Employee createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee) {
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
// get employee by id rest api
@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity < Employee > getEmployeeById(@PathVariable Long id) {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() - > new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id :" + id));
return ResponseEntity.ok(employee);
}
// update employee rest api
@PutMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity < Employee > updateEmployee(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Employee employeeDetails) {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() - > new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id :" + id));
employee.setFirstName(employeeDetails.getFirstName());
employee.setLastName(employeeDetails.getLastName());
employee.setEmailId(employeeDetails.getEmailId());
Employee updatedEmployee = employeeRepository.save(employee);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedEmployee);
}
// delete employee rest api
@DeleteMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity < Map < String, Boolean >> deleteEmployee(@PathVariable Long id) {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() - > new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id :" + id));
employeeRepository.delete(employee);
Map < String, Boolean > response = new HashMap < > ();
response.put("deleted", Boolean.TRUE);
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
}
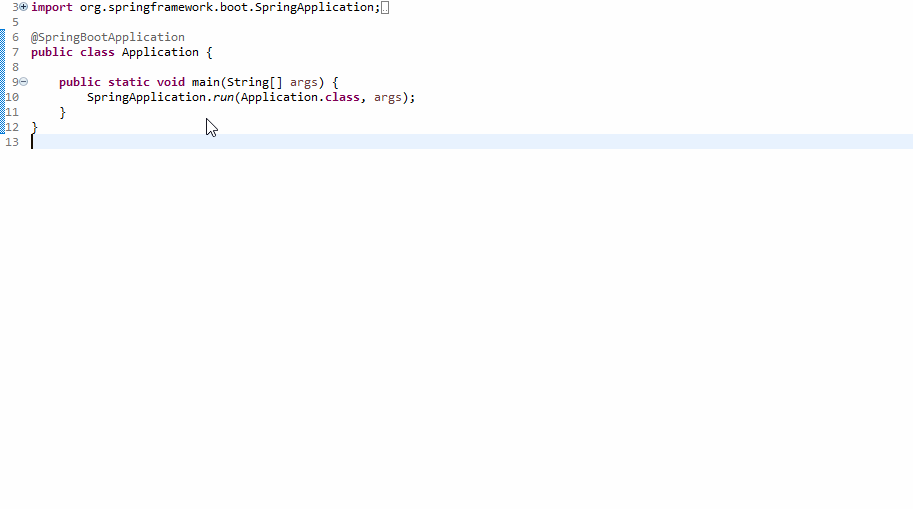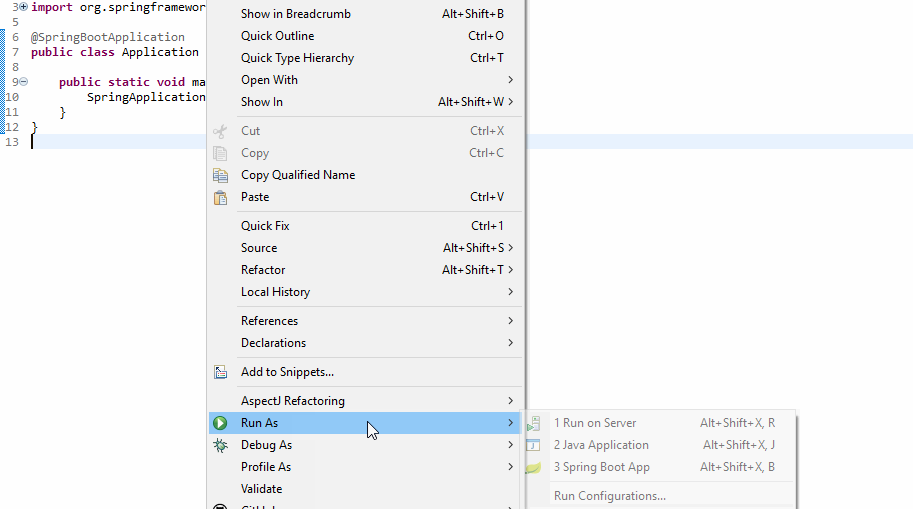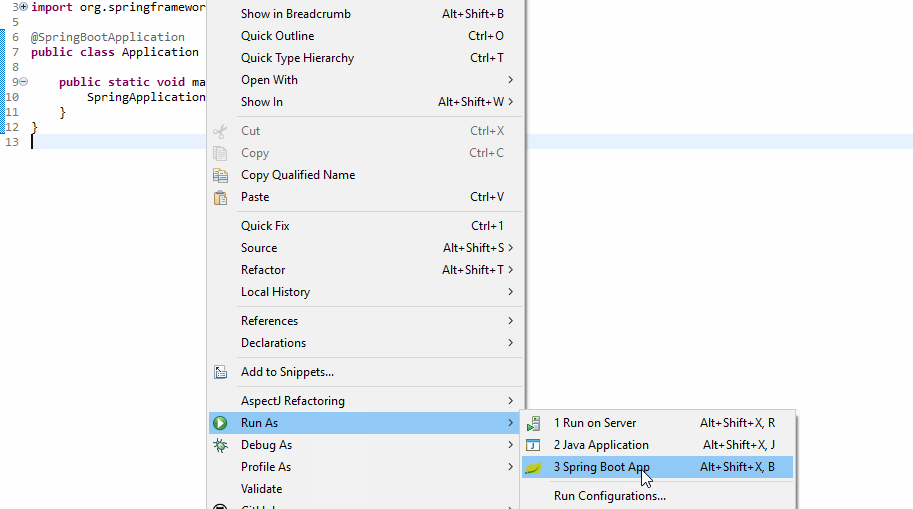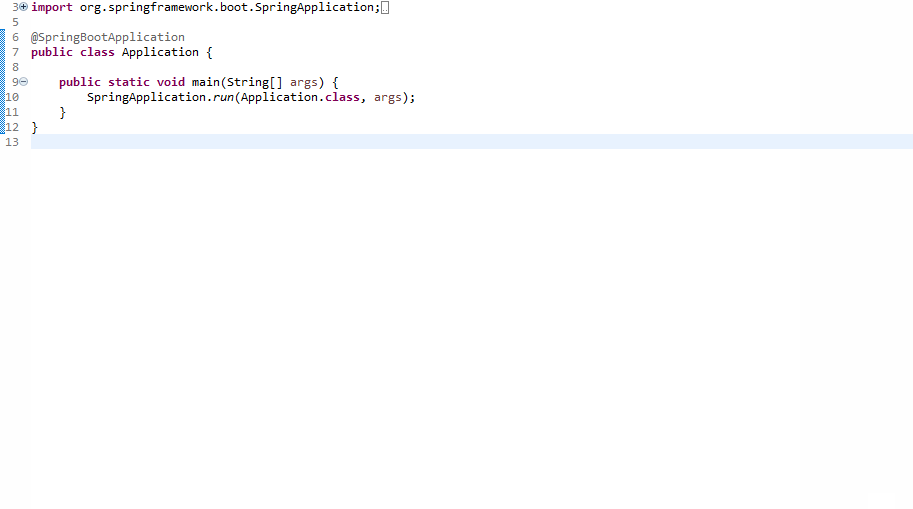
9. Running Application
This spring boot application has an entry point Java class called SpringbootBackendApplication with the public static void main(String[] args) method, which you can run to start the application.
package net.javaguides.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootBackendApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootBackendApplication.class, args);
}
}
Or you can start the spring boot application via the command line using the below command:
$ mvn spring-boot:runWhat’s Next?
In the next part of this series, we’ll learn how to develop React App with CRUD operations and how to consume REST APIs developed in this Spring boot project.




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)











Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment