🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In this tutorial, we will learn how to implement step by step many-to-many entity mapping using JPA/Hibernate with Spring Boot, Spring Data JPA, and MySQL database.
Learn Spring boot at https://www.javaguides.net/p/spring-boot-tutorial.html.
Learn Hibernate at https://www.javaguides.net/p/hibernate-tutorial.html
Video Tutorial
This tutorial explained in below youtube video:Overview
In many-to-many association, the source entity has a field that stores a collection of target entities. The @ManyToMany JPA annotation is used to link the source entity with the target entity.
A many-to-many association always uses an intermediate join table to store the association that joins two entities. The join table is defined using the @JoinTable JPA annotation.
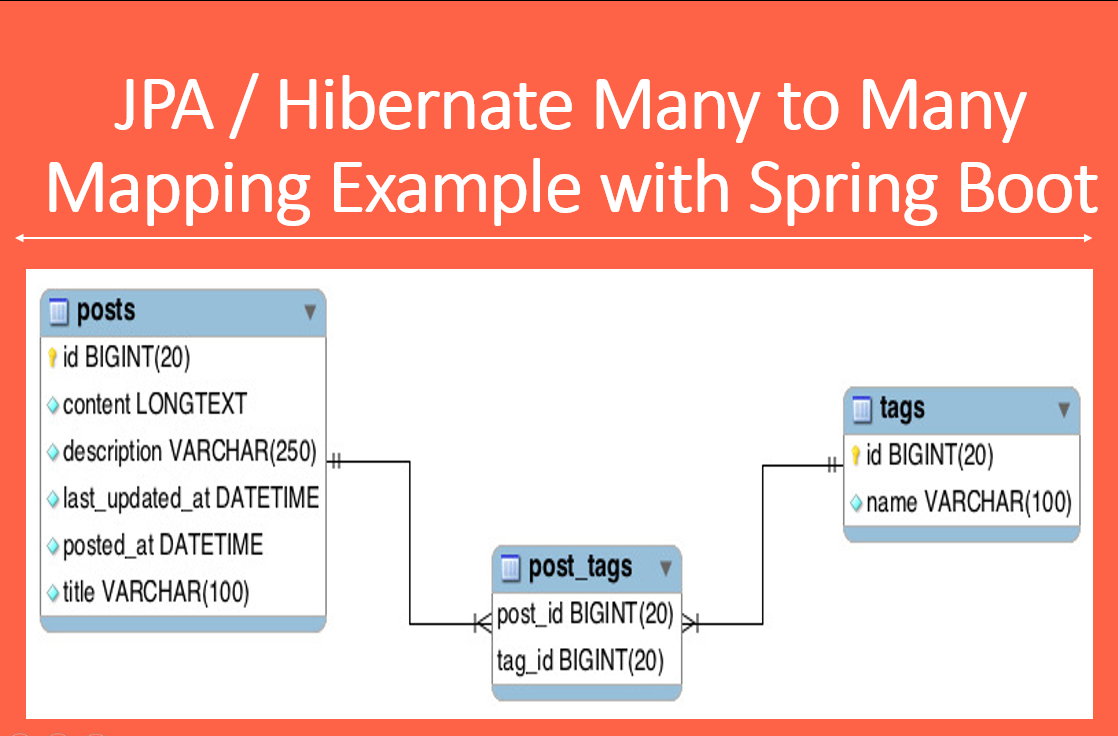
Consider the following tables where posts and tags exhibit a many-to-many relationship between each other:
The many-to-many relationship is implemented using a third table called post_tags which contains the details of posts and their associated tags.
Let’s now create a spring boot project from scratch and learn how to go about implementing such many-to-many relationships using JPA and Hibernate.
Tools and Technologies used
- Spring boot 2+
- Hibernate 5+
- JDK 1.8+
- Maven 3+
- IDE - STS or Eclipse
- Spring Data JPA
- MySQL 5+
Development Steps
- Create a Spring Boot Application
- Maven pom Dependencies
- Project Structure
- Configuring the Database and Hibernate Log levels
- Defining the Domain Models
- Defining the Repositories
- Run and Test the Application
1. Create a Spring Boot Application
There are many ways to create a Spring Boot application. You can refer below articles to create a Spring Boot application.
>> Create Spring Boot Project With Spring Initializer
>> Create Spring Boot Project in Spring Tool Suite [STS]
>> Create Spring Boot Project in Spring Tool Suite [STS]
2. Maven pom Dependencies
Let's add required maven dependencies to pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-hibernate-many-to-many-mapping</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-hibernate-many-to-many-mapping</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot Hibernate many to many mapping</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
3. Project Structure
Let's refer below screenshot to create our Project packaging structure:
4. Configuring the Database and Hibernate Log levels
We’ll need to configure MySQL database URL, username, and password so that Spring can establish a connection with the database on startup.
Open src/main/resources/application.properties and add the following properties to it:
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
## Hibernate Properties
We’ll need to configure MySQL database URL, username, and password so that Spring can establish a connection with the database on startup.
Open src/main/resources/application.properties and add the following properties to it -
# The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
logging.level.org.hibernate.SQL=DEBUG
Make sure that you change the spring.datasource.username and spring.datasource.password properties as per your MySQL installation. Also, create a database named demo.
The spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update property makes sure that the database tables and the domain models in your application are in sync. Whenever you change the domain model, hibernate will automatically update the mapped table in the database when you restart the application.
I have also specified the log levels for hibernate so that we can debug the SQL queries executed by hibernate.
5. Defining the Domain Models
Let’s define the domain models which will be mapped to the tables we saw earlier.
Let's create Post and Tag domain models.
Post.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.entity;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.JoinTable;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
/**
* Post domain model
* @author javaguides.net
*
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "posts")
public class Post {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(name = "title")
private String title;
@Column(name = "description")
private String description;
@Column(name = "content")
private String content;
@Column(name = "posted_at")
private Date postedAt = new Date();
@Column(name = "last_updated_at")
private Date lastUpdatedAt = new Date();
@ManyToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinTable(name = "post_tags",
joinColumns = {
@JoinColumn(name = "post_id")
},
inverseJoinColumns = {
@JoinColumn(name = "tag_id")
})
private Set < Tag > tags = new HashSet < > ();
public Post() {
}
public Post(String title, String description, String content) {
super();
this.title = title;
this.description = description;
this.content = content;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public Date getPostedAt() {
return postedAt;
}
public void setPostedAt(Date postedAt) {
this.postedAt = postedAt;
}
public Date getLastUpdatedAt() {
return lastUpdatedAt;
}
public void setLastUpdatedAt(Date lastUpdatedAt) {
this.lastUpdatedAt = lastUpdatedAt;
}
public Set < Tag > getTags() {
return tags;
}
public void setTags(Set < Tag > tags) {
this.tags = tags;
}
}
Tag.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.entity;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
/**
* Tag domain model
* @author javaguides.net
*
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "tags")
public class Tag {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
private String name;
@ManyToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, cascade = CascadeType.ALL, mappedBy = "tags")
private Set < Post > posts = new HashSet < > ();
public Tag() {
}
public Tag(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Set < Post > getPosts() {
return posts;
}
public void setPosts(Set < Post > posts) {
this.posts = posts;
}
}
We use @ManyToMany annotation to create a many-to-many relationship between two entities. In a bi-directional association, the @ManyToMany annotation is used on both the entities but only one entity can be the owner of the relationship.
The entity that specifies the @JoinTable is the owning side of the relationship and the entity that specifies the mappedBy attribute is the inverse side.
In the above example, the Post entity is the owner of the relationship, and the Tag entity is the inverse side.
6. Defining the Repositories
Let’s define the repositories for accessing the Post and Tag data from the database.
PostRepository.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.Post;
@Repository
public interface PostRepository extends JpaRepository<Post, Long>{
}
TagRepository.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.Tag;
@Repository
public interface TagRepository extends JpaRepository<Tag, Long>{
}
7. Run and Test the Application
Let's test our many-to-many association setup. This is our main entry point of the Spring boot project. To run spring boot project, just right-click on this file and run as Java application:
package net.javaguides.springboot;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.Post;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.Tag;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.PostRepository;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootHibernateManyToManyMappingApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private PostRepository postRepository;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootHibernateManyToManyMappingApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String...args) throws Exception {
Post post = new Post("Hibernate Many to Many Mapping Example with Spring Boot",
"Hibernate Many to Many Mapping Example with Spring Boot",
"Hibernate Many to Many Mapping Example with Spring Boot");
Post post1 = new Post("Hibernate One to Many Mapping Example with Spring Boot",
"Hibernate One to Many Mapping Example with Spring Boot",
"Hibernate One to Many Mapping Example with Spring Boot");
Tag springBoot = new Tag("Spring Boot");
Tag hibernate = new Tag("Hibernate");
// add tag references post
post.getTags().add(springBoot);
post.getTags().add(hibernate);
// add post references tag
springBoot.getPosts().add(post);
hibernate.getPosts().add(post);
springBoot.getPosts().add(post1);
post1.getTags().add(springBoot);
this.postRepository.save(post);
this.postRepository.save(post1);
}
}
Output:
Once the application starts, check the console for hibernate specific logs to see what SQL statements are executed by hibernate for the operations that we have performed in the run() method:




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)












Hi, Ramesh, May I know how to print those values in post_tags table on thymeleaf?
ReplyDeleteI tried a lot of method available but unable to get the result