🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In this tutorial, you will learn how to create CRUD REST APIs for crud database operations using Spring Boot 3, Hibernate and H2 in-memory database.
In this example, we are creating crud operations and exposing them through REST APIs so that UI clients can invoke these operations. The demo operations enable the clients to modify the product records in the database.
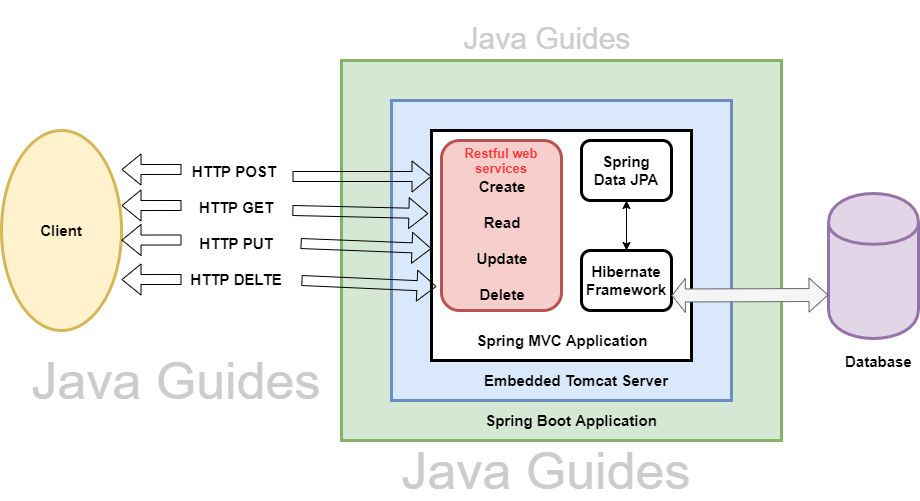
You can download the source code of this tutorial from my GitHub repository(link given at end of this tutorial.
Spring Boot CRUD Restful API with Hibernate

You can download the source code of this tutorial from my GitHub repository(link given at end of this tutorial.
Create Spring Boot Application
There are many ways to create a Spring Boot application. You can refer below articles to create a Spring Boot application.
Maven Dependencies
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>
- spring-boot-starter-web: It is used for building a web layer, including REST APIs, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Tomcat as the default embedded container.
- spring-boot-starter-data-jpa: It includes spring data, hibernate, HikariCP, JPA API, JPA Implementation (default is hibernate), JDBC and other required libraries.
- h2: Though we can add any database easily using data source properties in the application.properties file, we are using the h2 database to reducing unnecessary complexity.
Configure H2 Database
By default, Spring Boot configures the application to connect to an in-memory store with the username sa and an empty password. However, we can change those parameters by adding the following properties to the application.properties file:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
By design, the in-memory database is volatile and data will be lost when we restart the application.
We can change that behavior by using file-based storage. To do this we need to update the spring.datasource.url:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:file:/data/demo
In this example, we will use a default configuration of the H2 database (we don't use the above configuration, the above configuration is just to know more about H2 database configuration with Spring boot).
Create JPA Entity - Product.java
Let's create a Java class that represents an entity in a database. The annotations at the top of the class are used to map the class to a database table and define its properties.
package net.javaguides.springboot.model;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CreationTimestamp;
@Entity
@Table(name = "products")
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private long id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "description")
private String description;
@Column(name = "price")
private BigDecimal price;
@CreationTimestamp
private Date createdAt;
@CreationTimestamp
private Date updatedAt;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Date getCreatedAt() {
return createdAt;
}
public void setCreatedAt(Date createdAt) {
this.createdAt = createdAt;
}
public Date getUpdatedAt() {
return updatedAt;
}
public void setUpdatedAt(Date updatedAt) {
this.updatedAt = updatedAt;
}
}@Entity: This annotation marks the class as an entity that can be persisted to a database.
@Table(name = "products"): This annotation specifies the name of the table that corresponds to this entity in the database.
@Id: This annotation marks the field id as the primary key of the entity.
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO): This annotation specifies that the value of the primary key will be automatically generated by the database.
The JpaRepository interface provides several default methods for performing common database operations, such as save(), findById(), findAll(), and deleteById(). By extending this interface, the ProductRepository interface inherits these methods and can use them to interact with the database.
The two type parameters of the JpaRepository interface are specified in the ProductRepository interface:The first type parameter (Product) is the type of the entity that the repository manages.
The second type parameter (Long) is the type of the entity's primary key.
By defining this interface, the Spring Data JPA framework will automatically generate an implementation of the ProductRepository interface at runtime, which can be used to interact with the database. This allows developers to write code that interacts with the database using a simple, high-level API, without having to write low-level SQL statements.
Create a Spring Data Repository - ProductRepository.java
Let's create a ProductRepository interface that extends the JpaRepository interface, which is part of the Spring Data JPA framework.
The ProductRepository interface declares methods that can be used to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on entities of type Product in a database.
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Product;
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long> {
}
The two type parameters of the JpaRepository interface are specified in the ProductRepository interface:The first type parameter (Product) is the type of the entity that the repository manages.
The second type parameter (Long) is the type of the entity's primary key.
By defining this interface, the Spring Data JPA framework will automatically generate an implementation of the ProductRepository interface at runtime, which can be used to interact with the database. This allows developers to write code that interacts with the database using a simple, high-level API, without having to write low-level SQL statements.
Custom Exception - ResourceNotFoundException
package net.javaguides.springboot.exception;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1 L;
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message, Throwable throwable) {
super(message, throwable);
}
}Service Layer (uses repository)
The service layer is optional – still recommended to perform additional business logic if any. Generally, we will connect with repository here for crud operations.
ProductService.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.service;
import java.util.List;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Product;
public interface ProductService {
Product createProduct(Product product);
Product updateProduct(Product product);
List < Product > getAllProduct();
Product getProductById(long productId);
void deleteProduct(long id);
}
ProductServiceImpl.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import net.javaguides.springboot.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Product;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.ProductRepository;
@Service
@Transactional
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductRepository productRepository;
@Override
public Product createProduct(Product product) {
return productRepository.save(product);
}
@Override
public Product updateProduct(Product product) {
Optional < Product > productDb = this.productRepository.findById(product.getId());
if (productDb.isPresent()) {
Product productUpdate = productDb.get();
productUpdate.setId(product.getId());
productUpdate.setName(product.getName());
productUpdate.setDescription(product.getDescription());
productRepository.save(productUpdate);
return productUpdate;
} else {
throw new ResourceNotFoundException("Record not found with id : " + product.getId());
}
}
@Override
public List < Product > getAllProduct() {
return this.productRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Product getProductById(long productId) {
Optional < Product > productDb = this.productRepository.findById(productId);
if (productDb.isPresent()) {
return productDb.get();
} else {
throw new ResourceNotFoundException("Record not found with id : " + productId);
}
}
@Override
public void deleteProduct(long productId) {
Optional < Product > productDb = this.productRepository.findById(productId);
if (productDb.isPresent()) {
this.productRepository.delete(productDb.get());
} else {
throw new ResourceNotFoundException("Record not found with id : " + productId);
}
}
}
Spring REST Controller - ProductController
Finally, expose all operations through REST endpoints. Clients will connect with these endpoints to create/get/update/delete product records.
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Product;
import net.javaguides.springboot.service.ProductService;
@RestController
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("/products")
public ResponseEntity < List < Product >> getAllProduct() {
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(productService.getAllProduct());
}
@GetMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity < Product > getProductById(@PathVariable long id) {
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(productService.getProductById(id));
}
@PostMapping("/products")
public ResponseEntity < Product > createProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(this.productService.createProduct(product));
}
@PutMapping("/products/{id}")
public ResponseEntity < Product > updateProduct(@PathVariable long id, @RequestBody Product product) {
product.setId(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(this.productService.updateProduct(product));
}
@DeleteMapping("/products/{id}")
public HttpStatus deleteProduct(@PathVariable long id) {
this.productService.deleteProduct(id);
return HttpStatus.OK;
}
}
getAllProduct(): This method is mapped to a GET request to "/products" and returns a list of all products in the database. It returns a ResponseEntity object containing the list of products and an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
getProductById(long id): This method is mapped to a GET request to "/products/{id}" and returns a single product with the given ID. It returns a ResponseEntity object containing the product and an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
createProduct(Product product): This method is mapped to a POST request to "/products" and creates a new product with the given data. It returns a ResponseEntity object containing the newly created product and an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
updateProduct(long id, Product product): This method is mapped to a PUT request to "/products/{id}" and updates an existing product with the given ID using the data provided in the request body. It returns a ResponseEntity object containing the updated product and an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
deleteProduct(long id): This method is mapped to a DELETE request to "/products/{id}" and deletes the product with the given ID. It returns an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
The demo of this tutorial covered at Spring Boot CRUD Example with JPA and Hibernate - Video tutorial.
createProduct(Product product): This method is mapped to a POST request to "/products" and creates a new product with the given data. It returns a ResponseEntity object containing the newly created product and an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
updateProduct(long id, Product product): This method is mapped to a PUT request to "/products/{id}" and updates an existing product with the given ID using the data provided in the request body. It returns a ResponseEntity object containing the updated product and an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
deleteProduct(long id): This method is mapped to a DELETE request to "/products/{id}" and deletes the product with the given ID. It returns an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
Running Spring boot application
This spring boot application has an entry point Java class called SpringbootCrudHibernateExampleApplication.java with the public static void main(String[] args) method, which you can run to start the application.
package net.javaguides.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootCrudHibernateExampleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootCrudHibernateExampleApplication.class, args);
}
}
Download source code
The source code of this tutorial available on my
GitHub Repository.




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)










Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment