🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In this tutorial, we will learn how to build CRUD REST APIs using Spring Boot, JPA/Hibernate, and the PostgreSQL database. We will use the latest version of Spring Boot 3 in this tutorial.
YouTube Video
Before development, make sure that the PostgreSQL database is installed on your machine.
Check out these two links to download and install a PostgreSQL database on your machine.
- https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.3/tutorial-install.html
- http://www.postgresqltutorial.com/install-postgresql/
2. Tools and Technologies Used
- Spring Boot 3
- JDK - 17 or later
- Spring Framework
- Spring Data JPA (Hibernate)
- Maven
- IDE - Eclipse or Spring Tool Suite (STS)
- PostgreSQL
3. Development Steps
Step 1: Create a Spring Boot Application
Spring Boot provides a web tool called Spring Initializer to bootstrap an application quickly. Just go to https://start.spring.io/ and generate a new spring boot project.
Use the below details in the Spring boot creation:
Project Name: springboot-backend
Project Type: Maven
Choose dependencies: Spring Web, Spring Data JPA, PostgreSQL, Dev Tools
Package name: net.javaguides.springboot
Step 2: Maven dependencies
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-backend</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-backend</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Step 3: Configuring PostgreSQL Database
First, you need to create a database in the PostgreSQL server. You can use the following command to create a database in the PostgreSQL server:CREATE DATABASE employees;
Open the src/main/resources/application.properties file and add the following content to it:spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/employees
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
## Hibernate Properties
# The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
CREATE DATABASE employees;spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/employees spring.datasource.username=postgres spring.datasource.password=root spring.jpa.show-sql=true ## Hibernate Properties # The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect # Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
Step 4: Create JPA Entity - Employee.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email_address")
private String emailId;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String firstName, String lastName, String emailId) {
super();
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.emailId = emailId;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmailId() {
return emailId;
}
public void setEmailId(String emailId) {
this.emailId = emailId;
}
}Step 5: Create a Spring Data Repository - EmployeeRepository.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long>{
}Step 6: Create a Custom Exception
package net.javaguides.springboot.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}Step 7: Create Spring Rest Controller - EmployeeController.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import net.javaguides.springboot.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.EmployeeRepository;
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:4200")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
// get all employees
@GetMapping("/employees")
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees(){
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
// create employee rest api
@PostMapping("/employees")
public Employee createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee) {
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
// get employee by id rest api
@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> getEmployeeById(@PathVariable Long id) {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id :" + id));
return ResponseEntity.ok(employee);
}
// update employee rest api
@PutMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> updateEmployee(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Employee employeeDetails){
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id :" + id));
employee.setFirstName(employeeDetails.getFirstName());
employee.setLastName(employeeDetails.getLastName());
employee.setEmailId(employeeDetails.getEmailId());
Employee updatedEmployee = employeeRepository.save(employee);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedEmployee);
}
// delete employee rest api
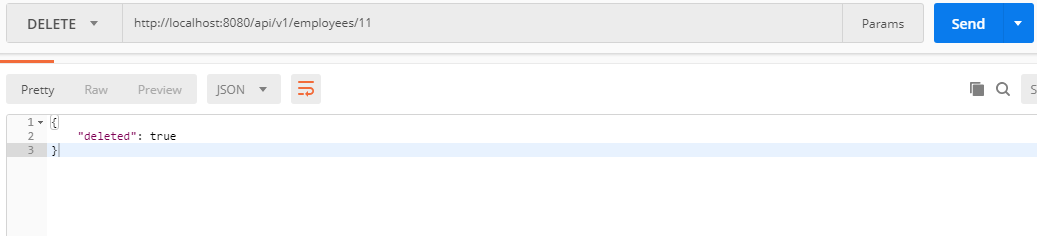
@DeleteMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Boolean>> deleteEmployee(@PathVariable Long id){
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id :" + id));
employeeRepository.delete(employee);
Map<String, Boolean> response = new HashMap<>();
response.put("deleted", Boolean.TRUE);
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
}Optional Step for Client Applications (React/Angular): Enable CORS on the Server
To enable CORS on the server, add a @CrossOrigin annotation to the EmployeeController:@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:4200")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/")
public class EmployeeController {
// ..
}
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:4200")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/")
public class EmployeeController {
// ..
}Step 8: Running Spring Boot Application
This spring boot application has an entry point Java class called SpringbootBackendApplication with the public static void main(String[] args) method, which you can run to start the application.package net.javaguides.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootBackendApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootBackendApplication.class, args);
}
}



![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)
















Good Tutorial, Thank you. :)
ReplyDeleteThanks
ReplyDeleteeasy understand tutorial, Thank you.
ReplyDeleteWhere is the implementation of findAll() method inside Repository class
ReplyDelete