🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
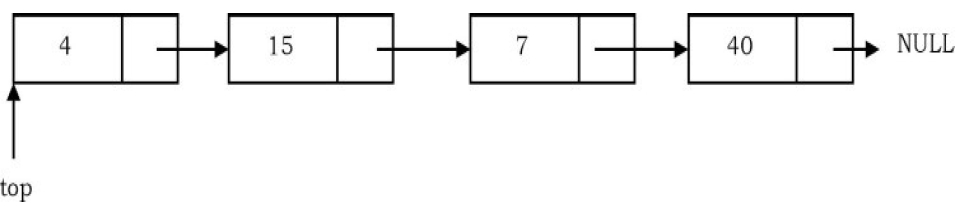
In this article, we will discuss Stack implementation using Linked List in Java. Instead of using an array, we can also use a linked list to implement a Stack. The linked list allocates the memory dynamically. However, time complexity in both scenarios is the same for all the operations i.e. push, pop, and peek.
In the linked list implementation of a Stack, the nodes are maintained non-contiguously in the memory. Each node contains a pointer to its immediate successor node in the Stack. A Stack is said to be overflown if the space left in the memory heap is not enough to create a node.
A push operation is implemented by inserting an element at the beginning of the list.
A pop operation is implemented by deleting the node from the beginning (the header/top node).
Why Linked List?
Using a linked list to implement a stack provides us with the ability to have a dynamically sized stack. This means we won't face the "stack overflow" issue if we reach a certain size, unlike array implementations.
Implementation of a Stack using Linked List in Java
Let's first create a Linked List Node class.
/**
* Class demonstrates the declaration for a linked list.
* @author Ramesh Fadatare
*
*/
public class ListNode{
public ListNode next;
public int data;
// Creates an empty node.
public ListNode(){
next = null;
data = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
// Creates a node storing the specified data.
public ListNode (int data){
next = null;
this.data = data;
}
// Returns the node that follows this one.
public ListNode getNext(){
return next;
}
// Sets the node that follows this one.
public void setNext (ListNode node){
next = node;
}
// Returns the data stored in this node.
public int getData(){
return data;
}
// Sets the data stored in this node.
public void setdata (int elem){
data = elem;
}
// Sets the data stored in this node.
public String toString (){
return Integer.toString(data);
}
}
Let's write a program to demonstrate Stack implementation using Linked List in Java.
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
import com.javaguides.javads.lists.ListNode;
/**
* An implementation of a Stack using a Linked List
* @author Ramesh Fadatare
*
*/
public class LinkedStack {
private int length; // indicates the size of the linked list
private ListNode top;
// Constructor: Creates an empty stack.
public LinkedStack() {
length = 0;
top = null;
}
// Adds the specified data to the top of this stack.
public void push(int data) {
ListNode temp = new ListNode(data);
temp.setNext(top);
top = temp;
length++;
}
// Removes the data at the top of this stack and returns a
// reference to it. Throws an EmptyStackException if the stack
// is empty.
public int pop() throws EmptyStackException {
if (isEmpty())
throw new EmptyStackException();
int result = top.getData();
top = top.getNext();
length--;
return result;
}
// Returns a reference to the data at the top of this stack.
// The data is not removed from the stack. Throws an
// EmptyStackException if the stack is empty.
public int peek() throws EmptyStackException {
if (isEmpty())
throw new EmptyStackException();
return top.getData();
}
// Returns true if this stack is empty and false otherwise.
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (length == 0);
}
// Returns the number of elements in the stack.
public int size() {
return length;
}
// Returns a string representation of this stack.
public String toString() {
String result = "";
ListNode current = top;
while (current != null) {
result = result + current.toString() + "\n";
current = current.getNext();
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedStack stack = new LinkedStack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.toString();
System.out.println("Size of stack is: " + stack.size());
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
System.out.println("Top element of stack is: " + stack.peek());
}
}
Output:
Size of stack is: 5
Top element of stack is: 3Performance
Let n be the number of elements in the stack. The complexities for operations with this representation can be given as:
- Space Complexity (for n push operations) O(n)
- Time Complexity of create Stack: DynArrayStack() O(1)
- Time Complexity of push() O(1) (Average)
- Time Complexity of pop() O(1)
- Time Complexity of top() O(1)
- Time Complexity of isEmpty() O(1)
- Time Complexity of deleteStack() O(n)
Comparing Array Implementation & Linked List Implementation
Array Implementation
- Operations take constant time.
- Expensive doubling operation every once in a while.
- Any sequence of n operations (starting from an empty stack) - “amortized” bound takes time proportional to n.
Linked List Implementation
- Grows and shrinks gracefully.
- Every operation takes constant time O(1).
- Every operation uses extra space and time to deal with references.




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)










Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment