🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
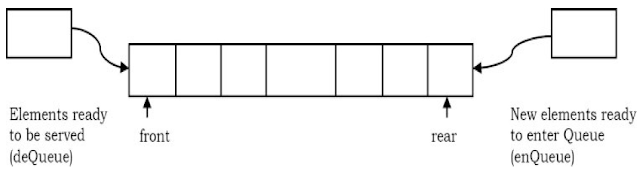
In this article, we will discuss dynamic queue implementation based on an array.
In the previous article, we have discussed queue implementation based on an fixed sized array.
In the previous article, we have discussed queue implementation based on an fixed sized array.
Dynamic Queue Implementation using Array
This program demonstrates the dynamic queue implementation based on an array. The capacity of the array will be increased when the queue is full.
Please refer to the comments are self-descriptive.
/**
* Dynamic Queue Implementation using Circular Array
* @author Ramesh Fadatare
*
*/
public class DynamicQueueImpl {
private int capacity = 2;
int queueArr[];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int currentSize = 0;
public DynamicQueueImpl(){
queueArr = new int[this.capacity];
}
/**
* this method adds element at the end of the queue.
* @param item
*/
public void enqueue(int item) {
if (isQueueFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is full, increase capacity...");
increaseCapacity();
}
rear++;
if(rear >= queueArr.length && currentSize != queueArr.length){
rear = 0;
}
queueArr[rear] = item;
currentSize++;
System.out.println("Adding: " + item);
}
/**
* this method removes an element from the top of the queue
*/
public void dequeue() {
if (isQueueEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Underflow ! Unable to remove element from Queue");
} else {
front++;
if(front > queueArr.length-1){
System.out.println("removed: "+queueArr[front-1]);
front = 0;
} else {
System.out.println("removed: "+queueArr[front-1]);
}
currentSize--;
}
}
/**
* This method checks whether the queue is full or not
* @return boolean
*/
public boolean isQueueFull(){
boolean status = false;
if (currentSize == queueArr.length){
status = true;
}
return status;
}
/**
* This method checks whether the queue is empty or not
* @return
*/
public boolean isQueueEmpty(){
boolean status = false;
if (currentSize == 0){
status = true;
}
return status;
}
private void increaseCapacity(){
//create new array with double size as the current one.
int newCapacity = this.queueArr.length*2;
int[] newArr = new int[newCapacity];
//copy elements to new array, copy from rear to front
int tmpFront = front;
int index = -1;
while(true){
newArr[++index] = this.queueArr[tmpFront];
tmpFront++;
if(tmpFront == this.queueArr.length){
tmpFront = 0;
}
if(currentSize == index+1){
break;
}
}
//make new array as queue
this.queueArr = newArr;
System.out.println("New array capacity: "+this.queueArr.length);
//reset front & rear values
this.front = 0;
this.rear = index;
}
public static void main(String a[]){
DynamicQueueImpl queue = new DynamicQueueImpl();
queue.enqueue(4);
queue.dequeue();
queue.enqueue(56);
queue.enqueue(2);
queue.enqueue(67);
queue.dequeue();
queue.enqueue(24);
queue.enqueue(98);
queue.dequeue();
queue.dequeue();
queue.dequeue();
queue.enqueue(435);
queue.dequeue();
queue.dequeue();
}
}
Output:
Adding: 4
removed: 4
Adding: 56
Adding: 2
Queue is full, increase capacity...
New array capacity: 4
Adding: 67
removed: 56
Adding: 24
Adding: 98
removed: 2
removed: 67
removed: 24
Adding: 435
removed: 98
removed: 435



![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)










Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment