🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (178K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
Introduction
In this article, you will learn what is a HashMap, how to create a HashMap, how to add new key-value pairs to a HashMap, how to remove keys from a HashMap, how to iterate over a HashMap, and how to create and store user-defined objects as keys in a HashMap, and much more.
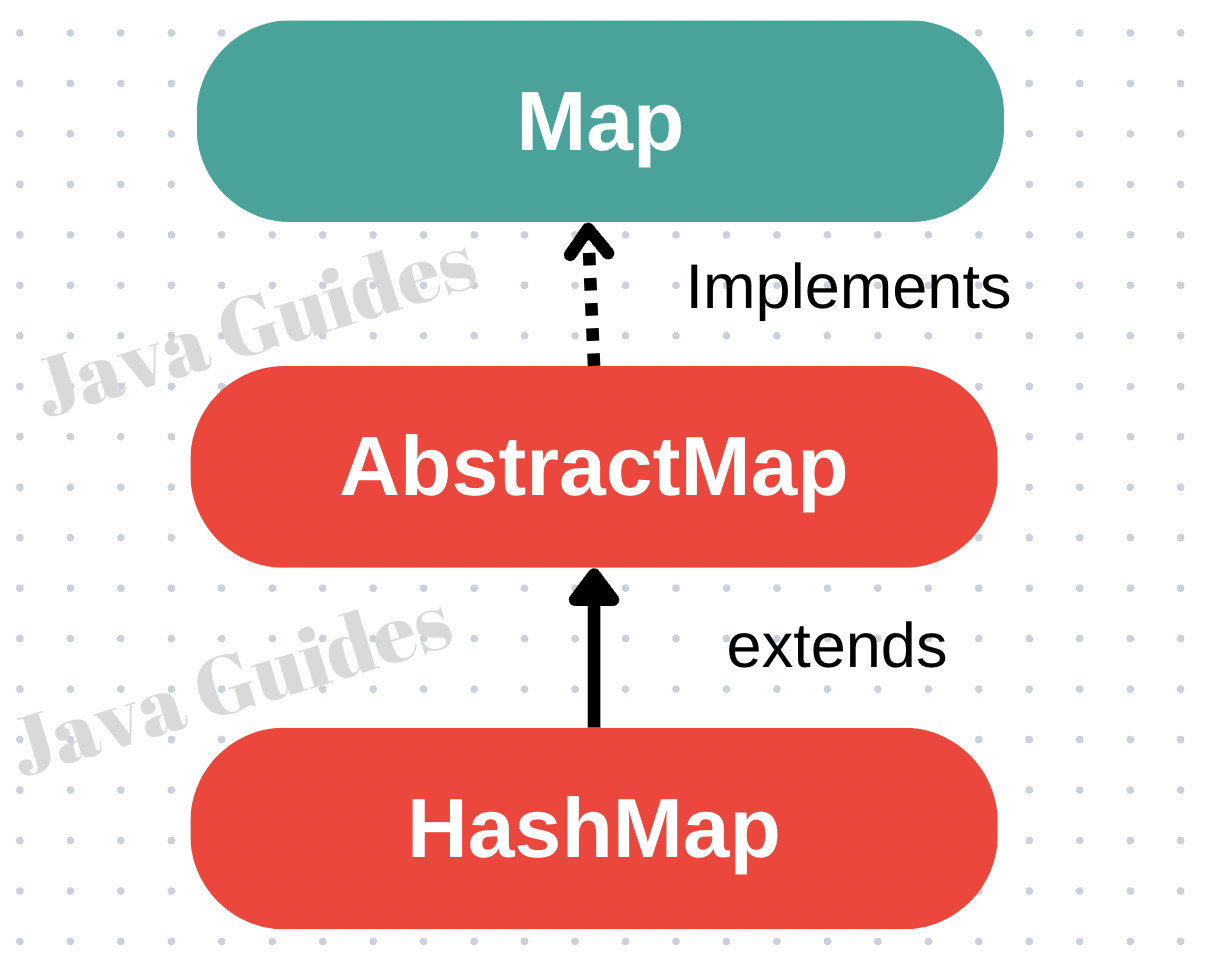
The HashMap class in Java is part of the Java Collections Framework and implements the Map interface. It provides the basic implementation of the Map interface of Java and is used to store data in the form of key-value pairs, which are known as entries.
HashMap uses a technique called Hashing, which allows us to access elements directly by calculating a unique key from their content. This unique key is the index at which the specific value is stored, making retrieval efficient.
Key Points About Java HashMap
Key-Value Pairs
HashMap stores data in key-value pairs. The key is used as an index to store data. The value is the actual object that the key is mapped to.
Null Keys and Values
HashMap allows one null key and multiple null values in a collection.
Non-Synchronized
HashMap is not synchronized, which means it is not thread-safe. If it is used in a multi-threaded environment, then it must be synchronized externally.
Insertion Order Not Preserved
The order in which keys or values are inserted into a HashMap is not necessarily the order in which they are iterated.
Unordered
HashMap does not guarantee any specific order of entries.
HashCode Method
The keys of HashMap are objects. Hence, these objects must implement the equals method and the hashCode method in order to follow the contract of the Map interface.
Performance
HashMap offers constant time performance for the basic operations get and put, assuming the hash function disperses the elements properly among the buckets.
Capacity and Load Factor
The capacity is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. Load factor is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to get before its capacity is automatically increased.
Implements
HashMap implements the Map interface and extends the AbstractMap class in Java.
Fail-Fast Iterator
The iterator of HashMap is fail-fast, meaning any structural modification (insertion or removal) after the creation of the iterator, will throw ConcurrentModificationException.
Creating a HashMap
Creating a HashMap in Java is straightforward. Here's an example:
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Adding Elements
You can add entries to the HashMap using the put() method. The put() method takes two parameters: the key and the corresponding value.
map.put("Apple", 10);
map.put("Orange", 20);
map.put("Banana", 30);
Here's the complete code with output:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Apple", 10);
map.put("Orange", 20);
map.put("Banana", 30);
System.out.println(map);
}
}
Output:
{Apple=10, Banana=30, Orange=20}
Note: The order in which entries are printed here does not represent the order in which they were inserted into the HashMap. This is because HashMap does not preserve the order of inserted entries.
HashMap Contains Null Key and Null Values
Here is an example that demonstrates how a HashMap can store null keys and null values:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a HashMap object
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
// Adding key-value pairs, including a null key and null values
map.put("Apple", "Red");
map.put(null, "Orange");
map.put("Banana", null);
map.put("Mango", "Yellow");
map.put("Pear", null);
System.out.println("HashMap: " + map);
}
}
In this program, a HashMap is created and then key-value pairs are added to it. Note the use of null as a key and null as values. The HashMap can store one null key and multiple null values.
When you run this program, you might see output like the following:
Output:
HashMap: {null=Orange, Pear=null, Apple=Red, Banana=null, Mango=Yellow}
Remember, the order of the elements in a HashMap is not guaranteed, so the order of the elements in your output may be different.
Access Elements in HashMap
To access elements in a HashMap, you can use the get() method. The get() method takes the key as an argument and returns the corresponding value.
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Apple", 10);
map.put("Orange", 20);
map.put("Banana", 30);
// Access the value corresponding to the key "Apple"
Integer appleValue = map.get("Apple");
System.out.println("Value for 'Apple': " + appleValue);
// Access the value corresponding to the key "Orange"
Integer orangeValue = map.get("Orange");
System.out.println("Value for 'Orange': " + orangeValue);
// Access the value corresponding to the key "Banana"
Integer bananaValue = map.get("Banana");
System.out.println("Value for 'Banana': " + bananaValue);
}
}
Output:
Value for 'Apple': 10
Value for 'Orange': 20
Value for 'Banana': 30
This output shows the values associated with the keys "Apple", "Orange", and "Banana" in the HashMap.
Note: If you attempt to access a key that does not exist in the HashMap using the get method, it will return null.
Remove Elements from HashMap
To remove an element from the HashMap, use the remove() method. The remove() method removes the mapping for a key from this map if it is present.
Here is the complete example:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a HashMap object
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// Add key-value pairs to the HashMap
map.put("Apple", 10);
map.put("Orange", 20);
map.put("Banana", 30);
System.out.println("Original HashMap: " + map);
// Remove the key-value pair with key "Apple"
map.remove("Apple");
System.out.println("HashMap after removing 'Apple': " + map);
// Remove the key-value pair with key "Orange"
map.remove("Orange");
System.out.println("HashMap after removing 'Orange': " + map);
}
}
This program creates a HashMap, adds some key-value pairs to it, and then removes some of these pairs. The remove() method takes a key as an argument and removes the corresponding key-value pair from the HashMap.
When you run this program, you should see the following output:
Output:
Original HashMap: {Orange=20, Banana=30, Apple=10}
HashMap after removing 'Apple': {Orange=20, Banana=30}
HashMap after removing 'Orange': {Banana=30}
HashMap Size
We can get the size of the HashMap using the size() method.
Here's a simple example of how to get the size of a HashMap in Java:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a HashMap object
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
// Adding key-value pairs to the map
map.put("Apple", "Red");
map.put("Orange", "Orange");
map.put("Banana", "Yellow");
map.put("Mango", "Yellow");
System.out.println("Original HashMap: " + map);
// Getting the size of the map
int size = map.size();
System.out.println("Size of the HashMap: " + size);
}
}
Output:
Original HashMap: {Mango=Yellow, Orange=Orange, Banana=Yellow, Apple=Red}
Size of the HashMap: 4
Iterate or Loop Through a HashMap
There are different ways we can loop through a HashMap:
- Using
entrySetand a for-each loop - Using
keySetand a for-each loop - Using
valuesand a for-each loop - Using an
Iterator - Using Java 8's
forEachmethod
Let's create a program that demonstrates the different ways to iterate over a HashMap in Java:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a HashMap
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Apple", "Red");
map.put("Orange", "Orange");
map.put("Banana", "Yellow");
// Using `entrySet` and a `for-each` loop:
System.out.println("Using `entrySet` and a `for-each` loop:");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey() + ", Value = " + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
// Using `keySet` and a `for-each` loop:
System.out.println("Using `keySet` and a `for-each` loop:");
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key = " + key + ", Value = " + map.get(key));
}
System.out.println();
// Using `values` and a `for-each` loop:
System.out.println("Using `values` and a `for-each` loop:");
for (String value : map.values()) {
System.out.println("Value = " + value);
}
System.out.println();
// Using an `Iterator`:
System.out.println("Using an `Iterator`:");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey() + ", Value = " + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
// Using Java 8's `forEach` method:
System.out.println("Using Java 8's `forEach` method:");
map.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("Key = " + key + ", Value = " + value));
}
}
Output:
Using `entrySet` and a `for-each` loop:
Key = Apple, Value = Red
Key = Orange, Value = Orange
Key = Banana, Value = Yellow
Using `keySet` and a `for-each` loop:
Key = Apple, Value = Red
Key = Orange, Value = Orange
Key = Banana, Value = Yellow
Using `values` and a `for-each` loop:
Value = Red
Value = Orange
Value = Yellow
Using an `Iterator`:
Key = Apple, Value = Red
Key = Orange, Value = Orange
Key = Banana, Value = Yellow
Using Java 8's `forEach` method:
Key = Apple, Value = Red
Key = Orange, Value = Orange
Key = Banana, Value = Yellow
Java HashMap with User-Defined Objects
If you are using user-defined objects as keys in your HashMap, you should make sure that these objects implement the equals() and hashCode() methods appropriately. If they do not, then your HashMap may not function as expected because it relies on these methods to store and retrieve objects.
Let's create a simple class named Employee:
class Employee {
private String id;
private String name;
Employee(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String getId(){
return this.id;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) obj;
return Objects.equals(id, employee.id) &&
Objects.equals(name, employee.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
And here is how to use Employee objects as keys in a HashMap:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Employee, String> employeeMap = new HashMap<>();
Employee e1 = new Employee("1", "John");
Employee e2 = new Employee("2", "Tom");
employeeMap.put(e1, e1.getName());
employeeMap.put(e2, e2.getName());
for (Map.Entry<Employee, String> entry : employeeMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
Output:
Employee{id='1', name='John'} : John
Employee{id='2', name='Tom'} : Tom
Conclusion
Congratulations folks! In this article, you learned what is a HashMap, how to create a HashMap, how to add new key-value pairs to a HashMap, how to remove keys from a HashMap, how to iterate over a HashMap, and how to create and store user-defined objects as keys in a HashMap.




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 4 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)










Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment